In this article I will give a detailed evaluation of Carat Weight, which is one of the most discussed points in the process of buying diamonds and customizing diamond rings.
Let's start with the below examples, which of the below sounds more impressive?
One-carat diamond
Diamond weighing one-fifth of a gram
200-milligram diamond
All three diamonds are the same weight. So if you thought one-carat diamond sounds more impressive, then you can understand why the jewelry industry prefers to use carats instead of grams to express gemstone weight. The term carat originated in ancient times when gemstones were weighed against the carob bean. Each bean weighed about one carat. In 1913, carat weight was standardized internationally and adapted to the metric system.
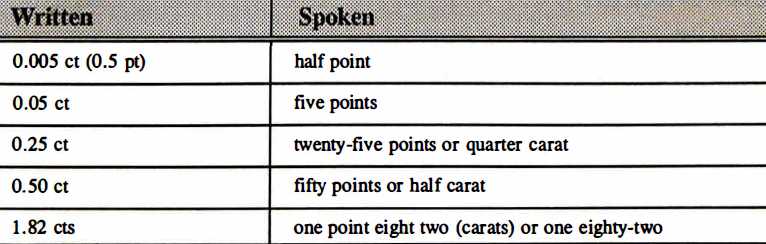
The weight of small diamonds is frequently expressed in points, with one point equaling 0.01 carats. For example, five points is a short way of saying five one-hundredths of a carat. Diamonds weighing 0.05 ct are referred to as five pointers.
Examine the following written and spoken forms of carat weight:
 |
| Table 1 |
Note that point when used in expressing weights over one carat refers to the decimal point, not a unit of measure. Also note that pt can be used instead of ct to make people think their diamond is 100 times heavier than it is.
Effect of Carat Weight on Price
Most people are familiar with the principle, the higher the carat weight the greater the diamond value. However, in actual practice, this principle is more complicated than it appears.
This can be illustrated by having you arrange the following four rings in the order of decreasing diamond value. Assume that the quality, shape and color of all the diamonds are the same.
a. 1-carat diamond solitaire ring (one diamond only)
b. 1-carat TW, 24-diamond wedding ring
C. 2-carat diamond solitaire ring
d. 2-carat TW, 48-diamond wedding ring
In almost all cases, the order of decreasing value would be c>a>d>b. In rare cases, the
order might be c> d>a>b. Strangely enough, a single one-carat diamond usually costs more than two carats of small diamonds of the same quality. This is because the supply of larger diamonds is limited. So when you compare ring prices, you should pay attention to individual diamond weights and notice the difference between the labels 1 ct TW (one carat total weight) and 1 ct (the weight of one stone). A ring with a 1 ct, colorless, top quality diamond can be worth more than 10 times as much as a ring with 1 ct TW diamonds of the same quality.
When comparing diamond cost, you should also start noting the per-carat cost instead of concentrating on the stone cost or the total diamond cost. To understand why, try comparing the cost of the following three diamonds. Assume they're the same color, shape and quality.
Weight Total Stone Cost
1.00 ct $6,000
1.20 ct $7,080
1.30 ct $7,540
Most people would find it hard to determine the best value just by looking at the total stone cost. Now try to compare values by looking at the per-carat cost of the same diamonds.
Weight Per-Carat Cost
1.00 ct $6.000
1.20 ct $5,900
1.30 ct $5,800
Normally, the 1.30 ct diamond should cost the same or more per-carat than the other two stones. However, in this case, it costs less. Consequently, the 1.30 ct stone is the best buy. But it's only when we compare the per-carat prices of the stones that this becomes evident.
Therefore when you shop for diamonds, think in terms of the per-carat cost. This is what diamond dealers do. To calculate the per-carat cost or the total cost of a diamond, use the following equations:
Per-carat cost = stone cost / carat weight
Total cost of a stone = carat weight x per carat cost
Diamonds can be divided into weight categories. These categories often vary from one dealer to another but may be outlined as follows:
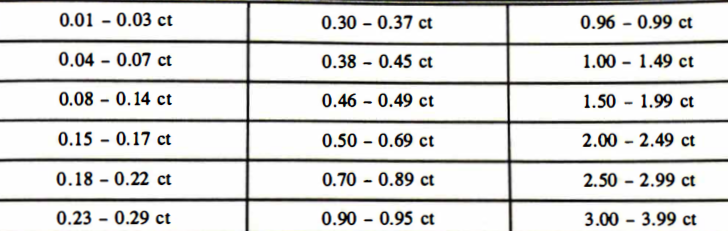 |
| Table 2 - Weight Categories for Diamonds |
The above weight categories are based mainly on those listed in the Rapaport Diamond Report. As diamonds move up from one weight category to another, their prices may increase from about 5% to 50%. So if you buy, for example, a 0.97 ct diamond instead of a 1 carat, you'll normally pay less per carat, even though the stone will resemble a one-carat diamond.
Low-quality diamonds tend to show less of a price differential between categories than those of high quality.
There are a couple exceptions to the rule that as diamond weight increases, per-carat value increases. Because of high demand, diamonds weighing 5, 10 or 15 points may cost more per carat than larger odd-size diamonds. Also, better quality .01 ct- to .035-ct diamonds have sometimes cost more per carat than diamonds weighing from .06 ct to .08 ct. This was the case during 1987-89, when there was an unusually high demand for three pointers for tennis bracelets.
The complexity of diamond pricing can be discouraging, but you don't need to know the details of the system to shop for value. Just be aware that carat weight as well as other factors can affect the per-carat value of diamonds and follow these two guidelines:
1. Compare the per-carat cost instead of the total cost. 2. When judging prices, compare diamonds of the same size, shape, quality and color.
Estimating Carat Weight
If you buy a diamond ring in a reputable jewelry store, you normally don't have to know how to estimate the carat weight of the diamonds because the weight will be marked on the ring. However, if you buy diamond jewelry at flea markets or auctions, it's to your advantage to know how to roughly estimate weight.
Probably the easiest way to estimate weight is to carry a diamond weight estimator with you. It's an inexpensive piece of metal or plastic that has cutouts or diagrams of diamond sizes corresponding to various diamond weights.
They can be found in jewelry supply stores. It shows the corresponding sizes of round-brilliant diamonds of various weights.
Weight estimators and charts which do not take into consideration the depth of a diamond or its girdle thickness can only give a general idea of the weight. (The girdle is the rim around the diamond.)
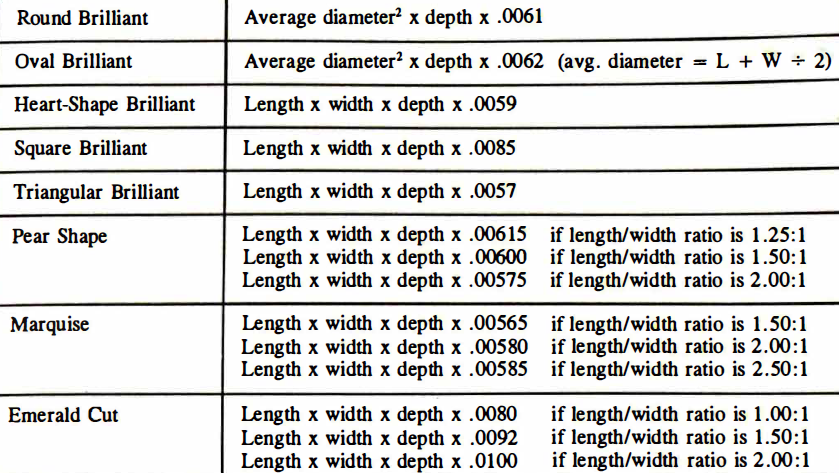
Weight can also be estimated by measuring the stone with a gauge and calculating its weight with formulas such as those in Table 3.
 |
|
Table 3 - These formulas were developed for stones with good proportions. Add 2% for slightly thick girdles and from 4% to 10% for thick to extremely thick girdles. Keep in mind that the only accurate means of determining the weight of a stone is to take it out of its setting and weigh it. This, however, is not always possible nor advisable. The source of these formulas is mainly the GIA Diamond Grading Laboratory Manual.
|
Size Versus Carat Weight
Sometimes in the jewelry trade, the term "size" is used as a synonym for "carat weight." This is because small round diamonds having the same weight also look the same size and have similar diameters. As diamonds increase in weight, their size becomes less predictable.
This means that a 0.90-carat round diamond can look bigger than a 1.00-carat round diamond, especially if the lighter-weight stone is cut shallow. So if size is important to you, consider diamond measurements as well as carat weight. You don't need to carry a millimeter gauge when you go shopping. Just start noting the different illusions of size that different diamond measurements can create. I will explain how diamond proportions affect size and beauty in next few articles.
Diamonds that look big for their weight may have reduced brilliance and fire. You should also note that diamonds usually have different measurements than other gemstones having the same weight. For example, because of its high density, a one-carat cubic zirconia is considerably smaller than a one-carat diamond.
On the other hand, a one-carat emerald, due to its lower density, is bigger than a one-carat diamond. We can compare gem sizes by comparing their specific gravity (the ratio of a gem's weight to the weight of an equal volume of water at 4 ). The specific gravity of diamond is 3.52 (t.01) whereas that of cubic zirconia is 5.80 (t.20) and that of emerald is 2.72 (+.18, -05).
In next few articles, you'll learn about a variety of diamond shapes and cutting styles. These, too, can play an important role in determining the apparent size of a stone.
 |
Fig.1 - A new style of brilliant cut, which is available in a variety of
shapes-(clockwise from top left) round, octagonal rectangle, pear shape, oval, marquise, octagonal square, and heart. This style has 105 facets and was named after its creator, the renowned master diamond cutter, Gabriel (Gabi) Tolkowsky. |
















































